栈
应用
表达式求值
1. 栈实现表达式求值
如果当前运算符优先级小于等于op栈顶的运算符,则弹出两个操作数和操作符进行运算
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int get_priority(char op) {
switch (op) {
case '(':
return 0;
case '*':
case '/':
return 2;
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
default:
return 0;
}
}
void operation(stack<int> &operand, stack<char> &op) {
int operand2 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
int operand1 = operand.top();
operand.pop();
char t = op.top();
op.pop();
cout << operand1 << t << operand2 << endl;
switch (t) {
case '+':
operand.push(operand1 + operand2);
break;
case '-':
operand.push(operand1 - operand2);
break;
case '*':
operand.push(operand1 * operand2);
break;
case '/':
operand.push(operand1 / operand2);
default:
break;
}
}
int main() {
string line;
stack<int> operand;
stack<char> op;
int result;
while (getline(cin, line)) {
cout << line << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < line.size(); ++i) {
if (line[i] >= '0' && line[i] <= '9') {
int num = 0;
while (line[i] >= '0' && line[i] <= '9') {
num = num * 10 + line[i] - '0';
i++;
}
--i;
operand.push(num);
cout << "push num:" << num << endl;
continue;
}
if (line[i] == ')') {
while (op.top() != '(') {
operation(operand, op);
}
op.pop();
continue;
}
if (!op.empty() &&
get_priority(line[i]) <= get_priority(op.top())) {
operation(operand, op);
}
op.push(line[i]);
cout << "push op:" << line[i] << endl;
}
while (!op.empty()) {
operation(operand, op);
}
cout << op.empty() << endl;
cout << operand.top() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
2. 递归下降
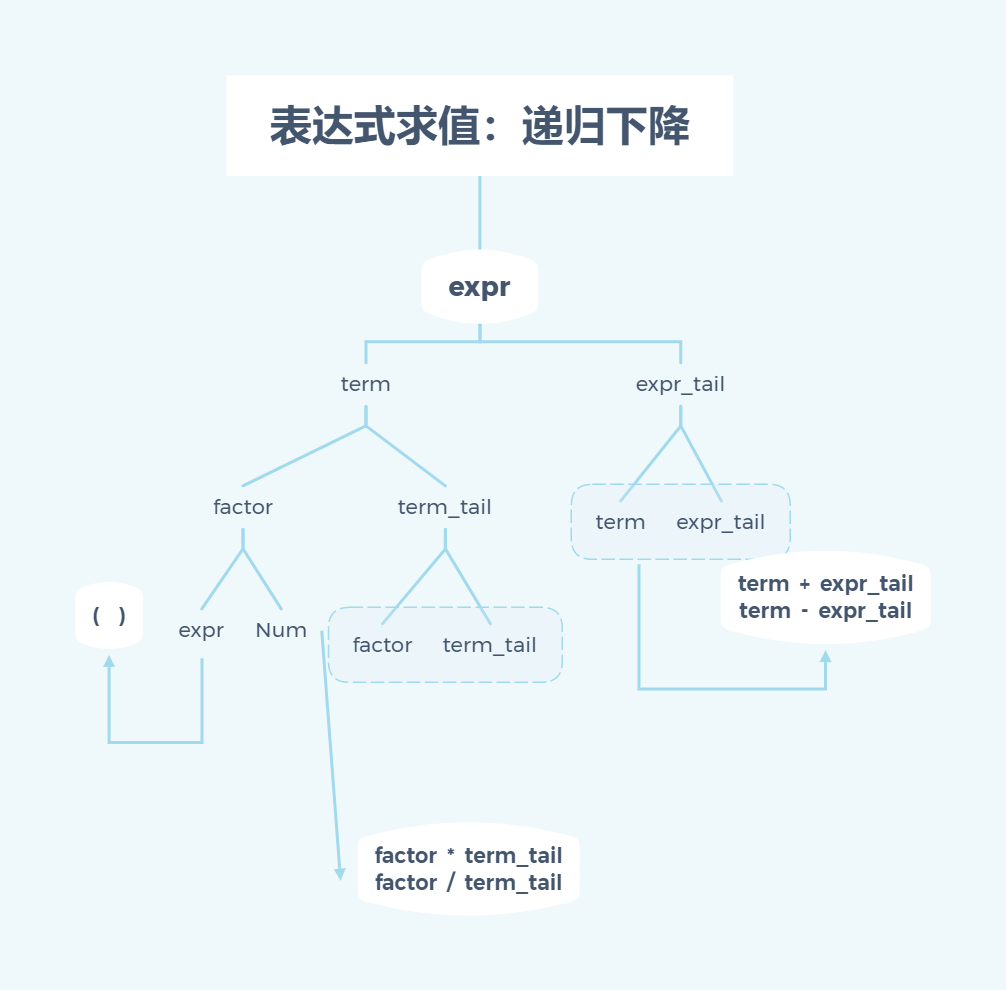
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum { Num };
char *src = NULL;
int token;
int token_val;
int expr();
void match(int tk);
void next();
int factor() {
int value = 0;
if (token == '(') {
match('(');
value = expr();
match(')');
} else {
value = token_val;
() printf("factor value;%d\n", value);
match(Num);
}
return value;
}
int term_tail(int lvalue) {
if (token == '*') {
match('*');
int value = lvalue * factor();
return term_tail(value);
} else if (token == '/') {
match('/');
int value = lvalue / factor();
return term_tail(value);
} else {
return lvalue;
}
}
int term() {
int lvalue = factor();
return term_tail(lvalue);
}
int expr_tail(int lvalue) {
if (token == '+') {
match('+');
int value = lvalue + term();
return expr_tail(value);
} else if (token == '-') {
match('-');
int value = lvalue - term();
return expr_tail(value);
} else {
return lvalue;
}
}
int expr() {
int lvalue = term();
return expr_tail(lvalue);
}
void match(int tk) {
if (token != tk) {
printf("excepted token: %d(%c), got %d(%c)\n", tk, tk, token, token);
exit(-1);
}
next();
}
void next() {
while (*src == ' ' || *src == '\t')
src++;
token = *src++;
if (token >= '0' && token <= '9') {
token_val = token - '0';
token = Num;
while (*src >= '0' && *src <= '9') {
token_val = token_val * 10 + *src - '0';
src++;
}
return;
}
printf("token:%d(%c) token_val:%d\n", token, token, token_val);
}
int main() {
char line[100];
while (gets(line)) {
src = line;
next();
printf("%d\n", expr());
}
return 0;
}
|
单调栈
单调栈通过维持栈内值的单调递增(递减)性,在O(n)的时间内处理需要大小比较的问题。
及时移除无用数据,保证栈/队列的有序性。
题目
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> secondGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n,-1);
stack<int> stk;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<>> pq;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int num=nums[i];
while(!pq.empty()&&pq.top().first<num){
auto [_,t]=pq.top();
pq.pop();
ans[t]=num;
}
while(!stk.empty()&&nums[stk.top()]<num){
pq.push({nums[stk.top()],stk.top()});
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
|

