1 线性表
2 线性链表
带表头结点
#include <iostream> using namespace std;struct Link_list { int data; Link_list *next; }; Link_list *Get_node () { Link_list *p = (Link_list *)malloc (sizeof (Link_list)); return p; } void Create_List (Link_list *&L, int n) L = (Link_list *)malloc (sizeof (Link_list)); L->next = NULL ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { Link_list *p = Get_node (); if (!p) cout << "分配结点失败" << endl; int t; cin >> t; p->data = t; p->next = L->next; L->next = p; } } void Show_List (Link_list *&L) Link_list *p = L->next; while (p) { cout << p->data << " " ; p = p->next; } cout << endl; } bool Get_node (Link_list *&L, int i, int &value) Link_list *p = L; while (i > 0 && p) { p = p->next; --i; } if (!p || i > 0 ) return false ; value = p->data; return true ; } bool Insert_node (Link_list *&L, int i, int e) Link_list *p = L, *t; while (p && i > 1 ) { p = p->next; --i; } if (!p || i > 1 ) { cout << "i不正确" << endl; return false ; } t = Get_node (); t->data = e; t->next = p->next; p->next = t; return true ; } bool Delete_node (Link_list *&L, int i, int &e) cout << "Delete:" << endl; Link_list *p = L; while (p && i > 1 ) { p = p->next; --i; } if (!p || i > 1 ) return false ; e = p->next->data; cout << "P->data:" << p->data << " e:" << e << endl; Link_list *t = p->next; p->next = t->next; free (t); return true ; } int main () Link_list *L; int n; cout << "要创建的结点数:" ; cin >> n; Create_List (L, n); Show_List (L); Insert_node (L, 3 , 100 ); Show_List (L); int value; Delete_node (L, 2 , value); Show_List (L); cout << "value: " << value << endl; return 0 ; }
3 双向链表
4 比较
数据结构
插入
删除
比较
线性表
O(n)
O(n)
移动元素
链表
O(n)
O(n)
寻找位置
双向链表
O(n)
O(n)
5 定义
链表有节点域和指针域两部分组成
precursor(pre,前驱)
successor(succ,后继)
dummy node(虚拟节点)
struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode (int x): val (x),next (nullptr ){} }
class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x){ val=x; next=null ; } }
6 题单
6.1 翻转链表
5.1.1.1.1 方法一:头插法
class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode *list=new ListNode (0 ),*p=head,*tmp; while (p){ tmp=p; p=p->next; tmp->next=list->next; list->next=tmp; } return list->next;; } };
5.1.1.1.2 方法二:迭代法
class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode *res=nullptr ,*tmp; while (head){ tmp=head->next; head->next=res; res=head; head=tmp; } return res; } };
5.1.1.1.3 方法三:递归法
class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (head==nullptr ||head->next==nullptr ){ return head; } ListNode* newHead=reverseList (head->next); head->next->next=head; head->next=nullptr ; return newHead; } };
6.2 合并链表
class Solution {public : ListNode* mergeTwoLists (ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) { ListNode* dummy=new ListNode (-1 ),*p=dummy; while (list1&&list2){ if (list1->val<=list2->val){ p->next=list1; list1=list1->next; }else { p->next=list2; list2=list2->next; } p=p->next; } p->next=list1?list1:list2; return dummy->next; } };
链表中点、链表原地翻转、链表合并
class Solution { struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode () : val (0 ), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x) : val (x), next (nullptr ) {} ListNode (int x, ListNode *next) : val (x), next (next) {} }; public : void reorderList (ListNode *head) if (head == nullptr ) return ; ListNode *mid = middleNode (head); ListNode *l1 = head, *l2 = mid->next; mid->next = nullptr ; l2 = reverseList (l2); mergeList (l1, l2); } ListNode *middleNode (ListNode *head) { ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head; while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr ) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; } ListNode *reverseList (ListNode *head) { ListNode *pre = nullptr , *cur = head; while (cur != nullptr ) { ListNode *nextTemp = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = nextTemp; } return pre; } void mergeList (ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) ListNode *p = l1, *q = l2; while (l1 && l2) { p = l1->next; q = l2->next; l1->next = l2; l2->next = p; l1 = p; l2 = q; } } };
方法一:哈希表方法二:双指针
假设链表 A 的头节点到相交点的距离是 a,链表 B 的头节点到相交点的距离是 b,相交点 到链表终点的距离为 c。我们使用两个指针,分别指向两个链表的头节点,并以相同的速度前进,若到达链表结尾,则移动到另一条链表的头节点继续前进。按照这种前进方法,两个指针会在 a +b +c 次前进后同时到达相交节点。
class Solution {public : ListNode *getIntersectionNode (ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { ListNode *h1=headA,*h2=headB; while (h1!=h2){ h1=h1==nullptr ?headB:h1->next; h2=h2==nullptr ?headA:h2->next; } return h1; } };
6.2.2 148. 排序链表
归并排序
class Solution {public : ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head) { return sortList (head,nullptr ); } ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head,ListNode* tail) { if (head==nullptr ) return head; if (head->next==tail){ head->next=nullptr ; return head; } ListNode* fast=head,*slow=head; while (fast!=tail){ slow=slow->next; fast=fast->next; if (fast!=tail) fast=fast->next; } ListNode* mid=slow; return mergeList (sortList (head,mid),sortList (mid,tail)); } ListNode* mergeList (ListNode* head1,ListNode* head2) { ListNode* dummy=new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode* p=dummy; while (head1&&head2){ if (head1->val<=head2->val){ p->next=head1; head1=head1->next; p=p->next; }else { p->next=head2; head2=head2->next; p=p->next; } } if (head1){ p->next=head1; }else if (head2){ p->next=head2; } return dummy->next; } };
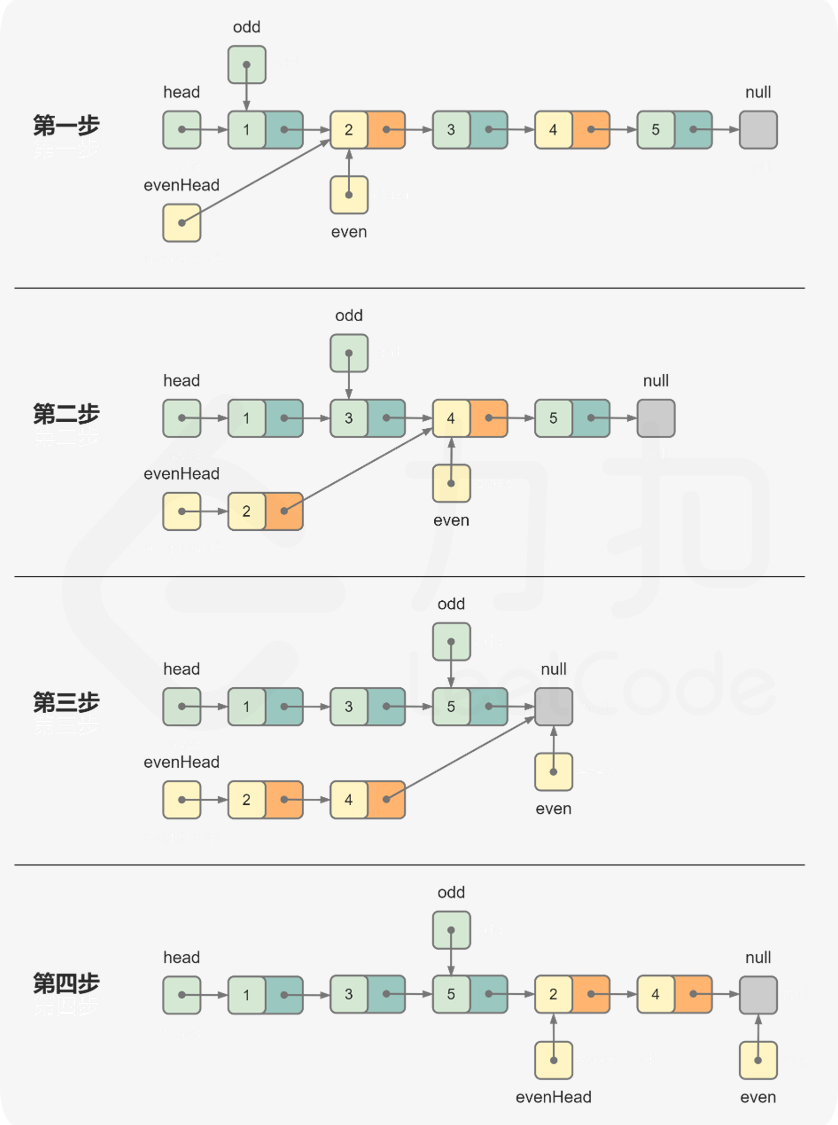
6.3 链表技巧
分离节点后合并
class Solution {public : ListNode* oddEvenList (ListNode* head) { if (head==nullptr ) return head; ListNode* evenHead=head->next; ListNode* odd=head,* even=evenHead; while (even&&even->next){ odd->next=even->next; odd=odd->next; even->next=odd->next; even=even->next; } odd->next=evenHead; return head; } };